2.2.3 Additional programming techniques
The Use of Basic String Manipulation in Python
Definition:
String manipulation is the process of changing, manipulating or processing text inputs in a program. In Python, there are various built-in string manipulation functions that can be used to perform common string operations.
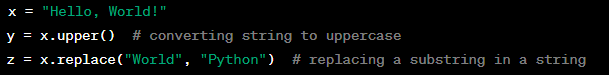
Example:
Significance:
String manipulation is important in programming as it allows you to manipulate or process text inputs in a program. With string manipulation functions, you can write programs that can process user inputs, manipulate data values, or display results in a specific format.
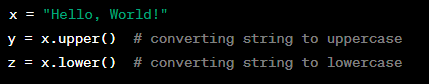
Converting Strings to Uppercase or Lowercase
Definition:
Converting strings to uppercase or lowercase involves changing all the characters in a string to uppercase or lowercase. In Python, this can be done using the upper() and lower() string methods.
Example:
Significance:
Converting strings to uppercase or lowercase can be useful in programming when you need to process text inputs or display results in a specific format. With these string methods, you can write programs that can process user inputs, manipulate data values, or display results in a specific format.
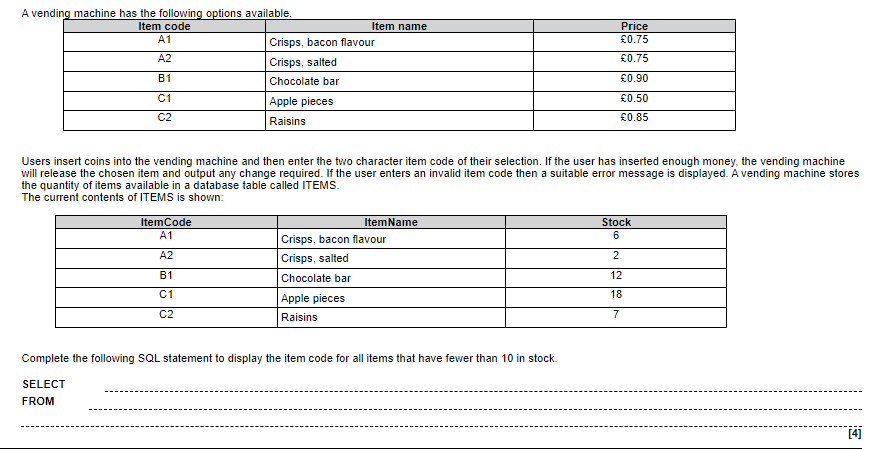
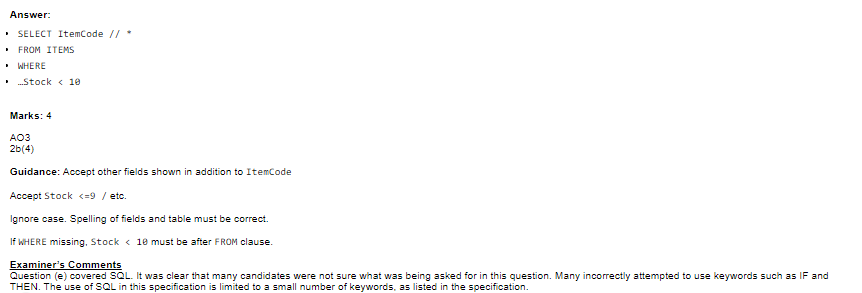
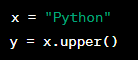
Practice Question:
![]()
Answer:
Replacing Substrings in a String
Definition:
Replacing substrings in a string involves changing a specific substring or pattern in a string with another substring or pattern. In Python, this can be done using the replace() string method.
Example:

Significance:
Replacing substrings in a string can be useful in programming when you need to manipulate text inputs or replace certain characters or patterns in a string. With the replace() string method, you can write programs that can process user inputs, manipulate data values, or display results in a specific format.
The Use of Basic File Handling Operations in Python
Definition:
File handling is the process of reading, writing, or manipulating files in a program. In Python, there are various built-in file handling functions that can be used to perform common file operations.
Example:
Significance:
File handling is important in programming as it allows you to read, write, or manipulate files in a program. With file handling functions, you can write programs that can read input files, manipulate data values, or generate output files.
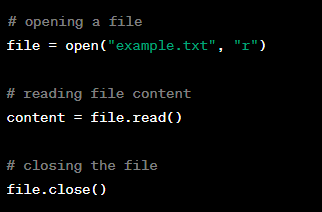
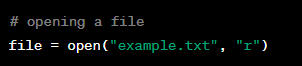
Opening a File in Python
Definition:
Opening a file in Python involves creating a connection between a file on disk and a variable in the program. This is done using the open() function in Python, which takes two arguments - the name of the file and the mode in which it should be opened (read, write, append, binary, etc.).
Example:
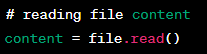
Reading a File in Python
Definition:
Reading a file in Python involves reading the contents of a file on disk into a variable in the program. This is done using the read() method on the file object.
Example:
Significance:
Reading a file in Python is useful when you need to process the contents of a file in a program. With the read() method, you can read the contents of a file on disk into a variable in the program, which allows you to manipulate or process the data.
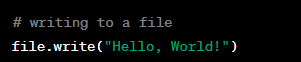
Writing to a File in Python
Definition:
Writing to a file in Python involves writing data from a variable in the program to a file on disk. This is done using the write() method on the file object.
Example:
Significance:
Writing to a file in Python is useful when you need to generate output files from a program. With the write() method, you can write data from a variable in the program to a file on disk, which allows you to save the output data for later use.
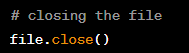
Closing a File in Python
Definition:
Closing a file in Python involves releasing the connection between the file on disk and the variable in the program. This is done using the close() method on the file object.
Example:
Records
In a database, a record (also known as a row) refers to a collection of related data fields that are grouped together to represent a single entity or instance of an object. Each field within a record corresponds to a specific attribute or characteristic of the entity, such as a person's name, age, address, etc.
A record is typically stored as a row within a database table, and each row represents a unique instance of the object being stored. For example, a database table for a school's student records might contain a row for each student, with fields for their name, age, grade level, etc.
Example of a record for a student in a school's database:
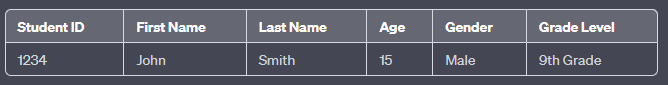
In this example, each column represents a field within the record for the student. The record contains information about the student's ID number, first and last name, age, gender, and grade level.
The Use of SQL to Search for Data
Definition:
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a programming language that is used to manage and manipulate data in a relational database. The SELECT, FROM, and WHERE clauses are fundamental components of SQL that are used to search for specific data within a database.
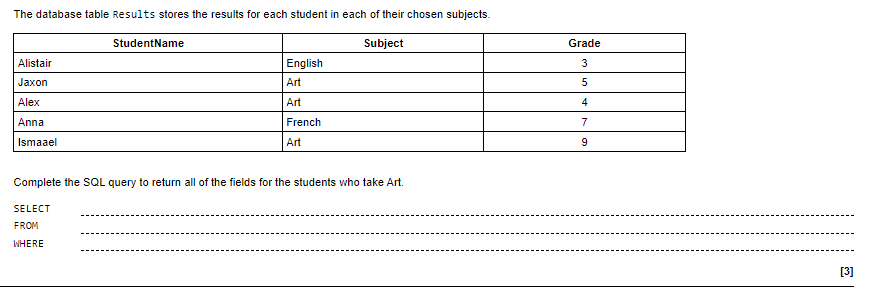
Example:
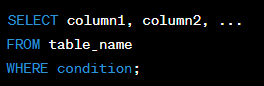
Significance:
SQL is an essential tool for managing large amounts of data within a relational database. With the SELECT, FROM, and WHERE clauses, you can search for specific data within a database and retrieve only the information that you need.
The SELECT Clause
Definition:
The SELECT clause is used to specify which columns of data should be retrieved from a database table.
Example:
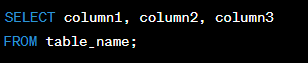
Significance:
The SELECT clause is important because it allows you to retrieve only the columns of data that you need from a database table. This can help to reduce the amount of data that needs to be processed and make database queries more efficient.
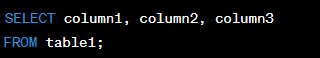
The FROM Clause
Definition:
The FROM clause is used to specify the database table or tables from which data should be retrieved.
Example:
Significance:
The FROM clause is important because it specifies the table or tables from which data should be retrieved. This allows you to search for data within a specific table or across multiple tables in a database.
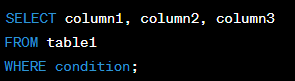
The WHERE Clause
Definition:
The WHERE clause is used to specify a condition that must be met in order for data to be retrieved from a database table.
Example:
Significance:
The WHERE clause is important because it allows you to search for data that meets specific criteria within a database table. This can help to narrow down the results of a database query and retrieve only the data that is relevant to your search.
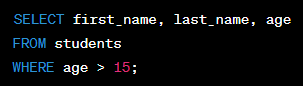
Using Select, From, and Where Together
Definition:
Using the SELECT, FROM, and WHERE clauses together allows you to search for specific data within a database and retrieve only the information that you need.
Significance:
Using the SELECT, FROM, and WHERE clauses together is important because it allows you to search for data that meets specific criteria within a database table and retrieve only the information that you need. This can help to reduce the amount of data that needs to be processed and make database queries more efficient.
Wildcard
In SQL, the wildcard character (*) is used in the SELECT statement to retrieve all columns of data from a database table. It represents a shortcut that allows you to retrieve all the available columns of data in a table without having to specify each column individually.
For example, if you wanted to retrieve all columns of data from a table named "students", you could use the following SQL query:
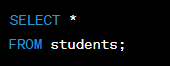
This would retrieve all the columns of data from the "students" table and return the results in a tabular format. It's worth noting that while the wildcard can be a convenient shortcut, it's generally considered best practice to specify the specific columns of data you need in your SQL queries, rather than relying on the wildcard. This can help to improve the performance of your database queries and make your code more maintainable in the long run.
The Use of Arrays in Problem Solving
Definition:
In programming, an array is a data structure that allows you to store multiple values of the same data type in a single variable. Arrays can be one-dimensional (1D) or two-dimensional (2D), depending on whether they have one or two indices.
Example:
![]()
Significance:
Arrays are important in programming because they allow you to store and manipulate large sets of data efficiently. They also provide a way to organize and access data in a structured manner, which can help to simplify complex algorithms and make them easier to understand.
One-Dimensional (1D) Arrays
Definition:
A one-dimensional (1D) array is a data structure that stores a collection of values in a single row or column.
Example:
![]()
Significance:
1D arrays are commonly used in programming to store and manipulate sets of data that can be represented as a single row or column. They are useful for tasks like storing and sorting lists of values, and can be used in a wide range of applications.
Two-Dimensional (2D) Arrays
Definition:
A two-dimensional (2D) array is a data structure that stores a collection of values in a grid or matrix with rows and columns.
Example:
![]()
Significance:
2D arrays are commonly used in programming to store and manipulate sets of data that can be represented as a grid or matrix. They are useful for tasks like storing and manipulating images, creating game boards, and working with tables of data.
Using Arrays in Problem Solving
Definition:
Using arrays in problem solving allows you to store and manipulate large sets of data efficiently and provides a way to organize and access data in a structured manner.
Example:
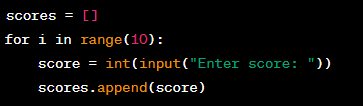
Significance:
Using arrays in problem solving is important because it allows you to store and manipulate sets of data in a way that is easy to understand and work with. By using arrays, you can perform tasks like sorting, searching, and filtering data, which are essential in many programming applications.
Conclusion
Arrays are a fundamental concept in programming, and understanding how to use them is essential for solving complex problems and building useful applications. By using one-dimensional (1D) and two-dimensional (2D) arrays, you can
Using Subprograms in Programming
Definition:
Subprograms are self-contained sections of code that can be called from within a program to perform a specific task. They are often referred to as functions or procedures, and are used to produce structured code.
Example:
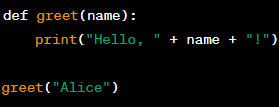
Significance:
Using subprograms in programming is important because it allows you to break down a large program into smaller, more manageable parts. By using functions or procedures, you can write code that is easier to read, debug, and maintain. Subprograms can also be reused across multiple programs, which can save you time and effort in the long run.
Functions
Definition:
A function is a subprogram that returns a value after performing a specific task. It can take one or more arguments as input, and can be called from within a program to perform a specific task.
Example:

Significance:
Functions are useful in programming because they allow you to perform complex calculations or operations in a single line of code. By encapsulating complex logic into a function, you can make your code easier to read, understand, and debug. Functions can also be reused across multiple programs, which can save you time and effort.
Procedures
Definition:
A procedure is a subprogram that performs a specific task without returning a value. It can take one or more arguments as input, and can be called from within a program to perform a specific task.
Example:
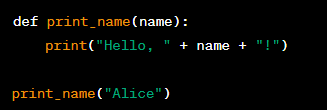
Significance:
Procedures are useful in programming because they allow you to perform specific tasks without returning a value. By encapsulating common operations into procedures, you can make your code easier to read, understand, and debug. Procedures can also be reused across multiple programs, which can save you time and effort.
Using Subprograms in Programming
Definition:
Using subprograms in programming is a way to produce structured code by breaking down a large program into smaller, more manageable parts. By using functions or procedures, you can write code that is easier to read, debug, and maintain.
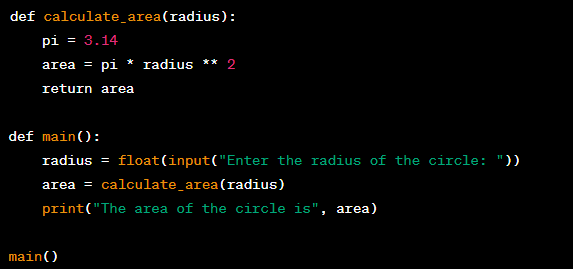
Random Number Generation in Programming
Definition:
Random number generation is a process of generating a sequence of numbers that cannot be predicted beforehand. In programming, this is often done using a random number generator function.
Example:
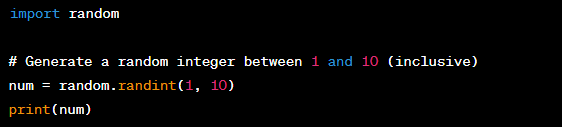
Significance:
Random number generation is useful in programming for a variety of purposes, including simulations, games, and encryption. By generating random numbers, we can simulate real-world situations or create unpredictable game elements that keep the player engaged. Random number generation can also be used to create strong encryption keys that cannot be easily guessed.
Past Exam Questions